“House of the sun”
Haleakala, Hawaiian for “House of the Sun,” appears like the perfect setting for a solar telescope. World famous for its amazing sunrises, the inactive volcano receives about 15 minutes more daylight than the sea-level part of the island of Maui.
According to Hawaiian tradition, the volcano took its name from a technique played on the sun by the demi-god Maui. Maui’s mom grumbled that the sun sped throughout the sky so quickly that her cloth might not dry. The trickster climbed up to the top of the mountain and lassoed the sun, refusing to release it until the sun consented to decrease. To secure his release, the sun accepted travel more gradually for
The spiritual significance of Hawaiian peaks has actually created chaos for other telescopes. Protests about the growing huge existence on Mauna Kea have halted construction of the Thirty Meter Telescope. Inouye didn’t get away opposition. In 2015 and 2017, hundreds of protesters collected to obstruct construction automobiles from taking a trip to the top of the peak.
Ever since, the telescope’s authorities have actually fulfilled two times a year with a working group of native Hawaiians, whom they intend to bring to see the ended up telescope. A new Science Support Center was also built at the base of the mountain to supply off-site support, and the peak stays available to native Hawaiians who wish to practice their religious beliefs on its slopes.
The National Solar Observatory has actually likewise assembled a set of lesson prepare for intermediate school instructors that highlight Hawaii’s long history of astronomy that was presented to regional instructors in 2019.
“We’ve been able to smooth over a lot of that contention,” Boboltz stated.
Follow Nola on Facebook and on Twitter at @NolaTRedd. Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook.
The Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope(DKIST), the world’s largest solar telescope, caught its very first image of The image starts what scientists hope will be a nearly 50-year research study of the Earth’s crucial star. The new images reveal little magnetic structures in incredible information. As construction on the 4-meter telescope unwind on the peak of
Inouye’s distinct resolution and sensitivity will enable it to penetrate the sun’s magnetic field for the really first time as it studies the activities that drive space weather in Earth’s community. Charged particles shed from the sun can hinder Earth’s mechanical satellites, power grids and communication facilities. The new telescope will likewise explore among the most counterintuitive solar secrets: why the sun’s corona, or external layer, is hotter than its noticeable surface.”These are the highest-resolution images and motion pictures of the solar surface area ever taken,” Inouye director Thomas Rimmele said throughout a news conference on Friday (Jan. 24). “Up to now, we’ve just seen the pointer of the iceberg.”
Related:
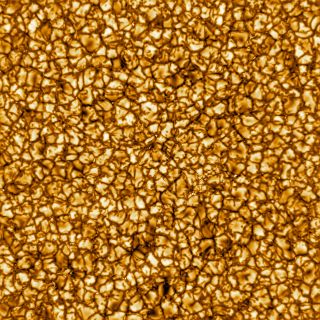
Ever since, the telescope has remained on budget plan and on schedule, according to Dave Boboltz, the program director for the National Science Foundation Astronomy Division. The telescope captured the freshly launched image, which is its first engineering image, on Dec. 10, 2019, but the observatory is not yet total. Only a single instrument, the Visible Broadband Imager(VBI), was functional at that time. The VBI takes extremely high-resolution images of the solar surface and lower atmosphere. The observatory’s second instrument, the Visible Spectro-polarimeter (VISP), started operation on Thursday( Jan. 23). Like a prism, VISP divides light into its part colors to offer precise measurements of its qualities along several wavelengths. The remaining instruments will be switched on as building and construction continues the 13-story structure, with full operations prepared to begin in July 2020.”We’re now in the final sprint of a long marathon, “Rimmele said. The very first light-images captured are a false color picture of the sun. The images were just processed but not examined for scientific outcomes because the building is still under building. However, Rimmele said that the magnetic structures that formerly appeared in solar images as single brilliant points are now noticeable as a number of smaller sized structures, offering a hint the new solar telescope’s abilities.
The next instrument that will be delivered to the summit will be the Cryogenic Near Infrared Spectra-Polarimeter, which will study the solar environment at infrared wavelengths, in order to probe electromagnetic fields in the sun’s corona over a big field of view. Quickly after, the Diffraction Limited Near Infrared Spectrom-Polarimeter will arrive, eventually using optical fibers to collect spectral information at every point in a two-dimensional solar image, enabling it to all at once measure spectral and spatial details. The last instrument, the Visible Tunable Filter, will capture very high-resolution pictures of the sun while performing high speed scans of the light that can identify atoms and particles.
Inouye is suggested to run for 44 years, which ought to cover two of the sun’s full 22-year solar cycles. Its suite of instruments will likely change gradually.
“The real power in the Inouye Solar Telescope is its versatility, its upgradability,” Boboltz said. “It’s like having a Swiss Army Knife to study the sun.” (this.src & & this.src.indexOf(‘missing-image. svg’ )!= =-1); this.parentNode.replaceChild(window.missingImage (), this)”sizes= “vehicle “data-normal= “https://vanilla.futurecdn.net/space/media/img/missing-image.svg “data-src =”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-320-80.jpg” data-srcset=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-320-80.jpg 320w, https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-650-80.jpg 650w, https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-970-80.jpg 970w”data-sizes=” vehicle”data-original-mos =”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd.jpg”data-pin-media=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd.jpg”> A close-up of the solar telescope’s very first released image.(Image credit: NSO/NSF/AURA )Solar solver The sun continuously sheds material into area in all directions. This continuous solar wind communicates with the Earth’s magnetic field, triggering the auroras. Other outbursts are more dramatic. Periodically, the sun will spit out big chunks of plasma and particles understood as coronal mass ejections (CMEs ); if these reach Earth, they can affect satellites and power grids, with the most effective triggering blackouts. Among the best-known modern catastrophes happened in 1989 when a geomagnetic storm hit Quebec, triggering a nine-hour blackout across the Canadian area. Research studies have actually set the expense of a prevalent blackout from 10s of billions to trillions of dollars, depending on the scenarios. Such effects might become more extreme.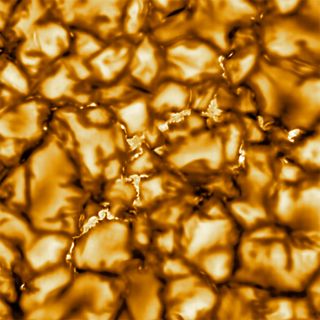
, solar flares triggered numerous radio blackouts on the sunlit side of Earth. Numerous radio blackouts halted interactions during the dangerous time, sometimes for as long as 8 hours.”A naturally occurring event in the world and a naturally occasion on the sun, when combined, represent a much bigger hazard to our society,” National Science Foundation Director Valentin Pillet said during the press conference. An infographic shows the scale of the features recorded in the recently released image. (Image credit: NSO/NSF/AURA)
The Inouye telescope ought to enable astronomers to find out more about what drives area weather condition. This understanding might help speed predictions for the most severe events, permitting a faster reaction during harmful circumstances.
Inouye will not act alone to accomplish this. “To actually understand the drivers and the impact of area weather condition, we require to utilize 2 complementary approaches,” Pillet stated. Inouye will deal with the first, making in-depth observations of the magnetic surface of the sun.
The second technique needs sending spacecraft near to the sun.
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe launched in 2018 and will get within 4 million miles (6 million kilometers) at its closest technique to the star. In February, NASA and the European Space Agency will introduce the Solar Orbiter, a mission committed to studying the sun’s heliosphere, the bubble of charged particles blown into space by the solar wind.
The trio are “really complementary in various ways,” Pillet stated. While Inouye will supply a detailed take a look at the sun’s electromagnetic field, the area objectives will position its observations in context with solar activity and solar weather. Together, “they will be at the leading edge of discovery for the next half century,” Pillet stated. “It truly is a terrific time to be a solar astronomer,” he said. Related: “auto Vehicledata-normal= “https://vanilla.futurecdn.net/space/media/img/missing-image.svg “data-src =”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-320-80.jpg” data-srcset=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-320-80.jpg 320w, https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-650-80.jpg 650w, https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd-970-80.jpg 970w”data-sizes=” autoVehicledata-original-mos =”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd.jpg”data-pin-media=”https://cdn.mos.cms.futurecdn.net/K97R8aj9vHhW6etEAomGDd.jpg”> A close-up of the solar telescope’s first very first released.(Image credit: NSO/NSF/AURA )Solar solver The sun constantly sheds material into area in all instructions.
from WordPress http://troot.net/worlds-largest-solar-telescope-produces-never-before-seen-image-of-our-star-space-com/
Keine Kommentare:
Kommentar veröffentlichen